Growing Peas Successfully
Sowing, care, harvest
Contents
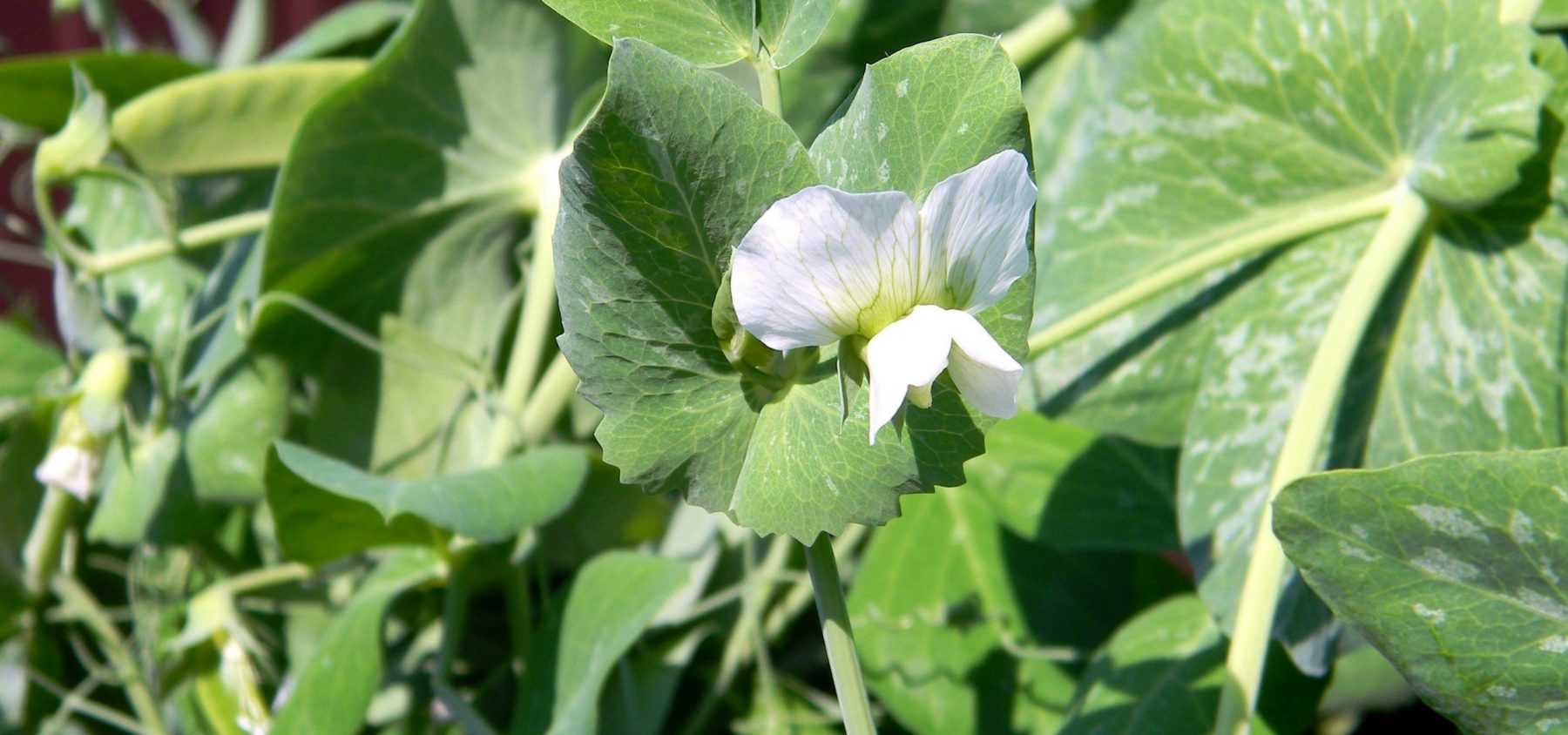
The pea is easy to grow and can be sown in a vegetable garden or in a pot on a balcony. However, it’s important to consider certain factors such as soil, watering, sowing distance and staking. Follow our advice to successfully sow peas and get a good harvest.
Which variety to choose?
Smooth-seeded peas (‘d’Annonay’ for example) are cold-resistant but dislike heat. They are perfect for early sowings. Conversely, wrinkled-seeded peas (like ‘Kelvedon Wonder’) tolerate heat but are less hardy: they are better suited to late spring sowings. Choose your variety according to your desired sowing date.
Read also
Staking climbing vegetable varietiesWhere to sow peas?
Peas thrive in mild and humid climates. They are not very demanding and grow well in all types of soil, even average ones, but they prefer light, cool and not overly chalky soils. Like most vegetable plants, they need sunlight to bear fruit.
In the vegetable garden, peas make good companions, as they associate well with almost all vegetables. However, avoid planting them near leeks, garlic, onions, shallots, fennel, and other Fabaceae like beans.
Discover other Peas
View all →Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
How to care for them?
Peas don’t require any particular maintenance apart from regular weeding and hoeing, which can be avoided if you mulch the soil.
The plants need support to cling to, especially in windy locations. For dwarf varieties like ‘Petit Provençal’, plant some small branched twigs, and for climbing varieties like ‘Serpette Guilloteaux‘ or ‘Express à longue cosse‘, provide stakes 1.5 to 2 metres tall or pea netting.
→ Discover our tutorial to build a tepee for climbing varieties.
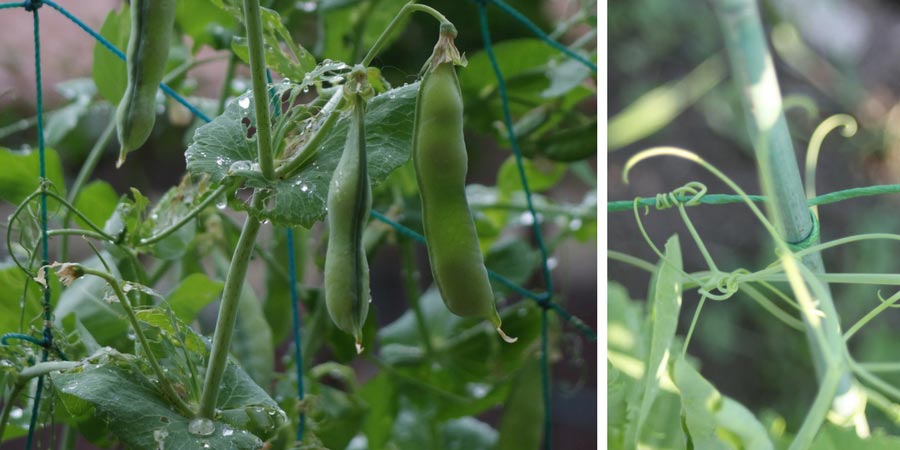

Peas climbing on pea netting
When growing peas, they particularly dislike both drought and waterlogging: don’t let the soil dry out and water regularly, but moderately until the pods form.
Potential pests and diseases
Peas generally grow without any issues. However, potential pests include:
- birds and slugs,
- green aphids, thrips, and pea moths.
To protect your seedlings, use insect-proof netting and apply an organic slug repellent such as Ferramol. Against green aphids and thrips, spray a solution of water mixed with black soap (20% dilution). Finally, to combat pea moths, use Bacillus thuringiensis—this organic insecticide is effective against caterpillars in general.
The most common disease is powdery mildew. This fungal disease can easily be avoided by not wetting the foliage and respecting planting distances.
Lastly, to maximise your chances of success, choose particularly resistant varieties, such as ‘Telephone à Rames’.
- Subscribe!
- Contents











































