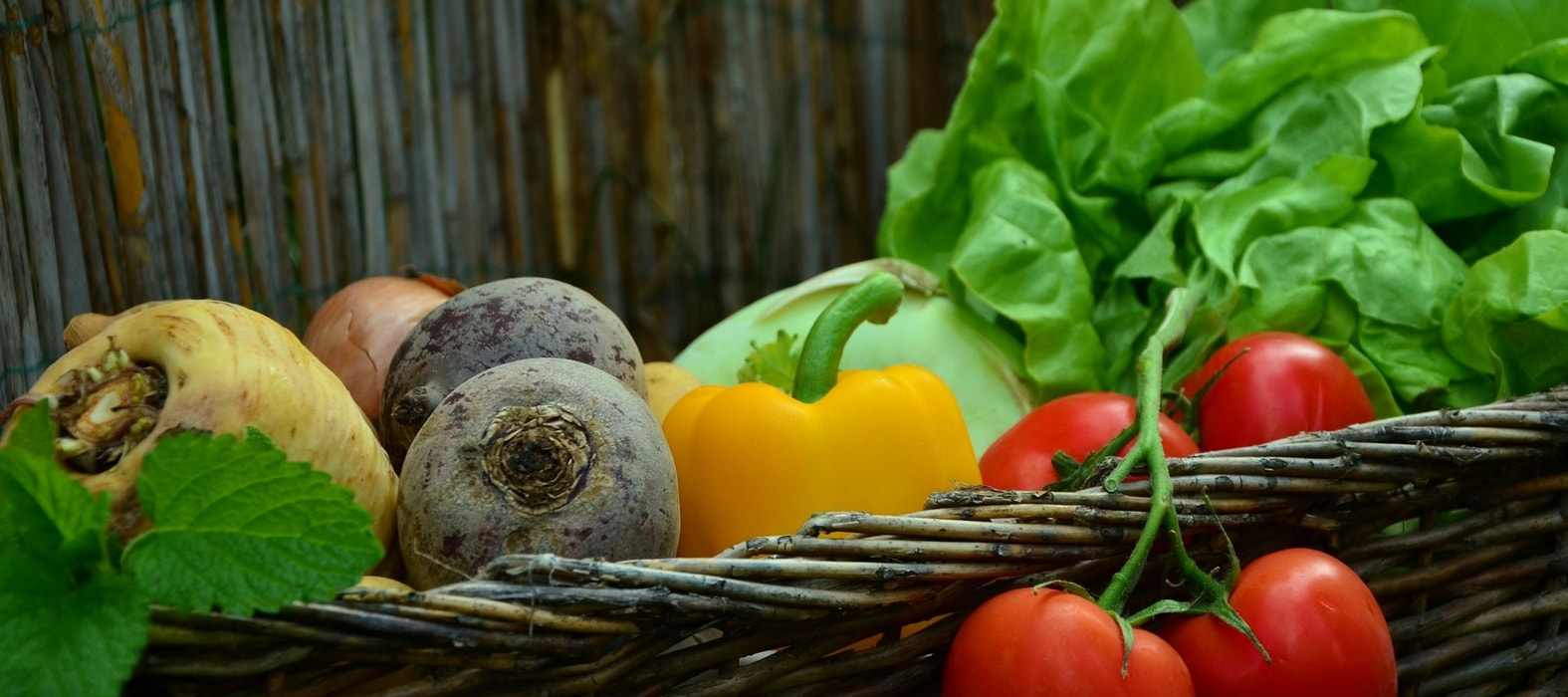

Conserver les légumes du potager
where and how? In the garden or at home?
Contents
To enjoy vegetables harvested from the vegetable garden throughout the year, it is essential to store them properly. For this, it is important to adapt the storage method to each case, as there is not one, but several ways.
Here are some simple and effective methods to keep your garden produce in reserve.
Keep vegetables in place, directly in the ground.
This method involves leaving vegetables in the ground, at the place where they were grown, protecting them, in the coldest climates, with a possible earthing up, a thick mulch, and/or by laying a fleece cover.
This type of preservation concerns, for example, cabbages, carrots, parsnips, leeks, but also spinach, lamb’s lettuce…
In the garden, in gauge
This method of preservation involves burying, either partially or completely, the vegetables that have been harvested. To do this, a cavity 30 to 40 cm deep is dug, the vegetables are placed inside, and then covered with fine soil followed by a frame or a thick layer of straw: they will be better protected from frost.
The storage method is reserved for light, well-draining soils and certain vegetable plants such as celery with midribs, fennel, salsify…
Discover other Vegetable gardens
View all →Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
In the cellar or in the garage
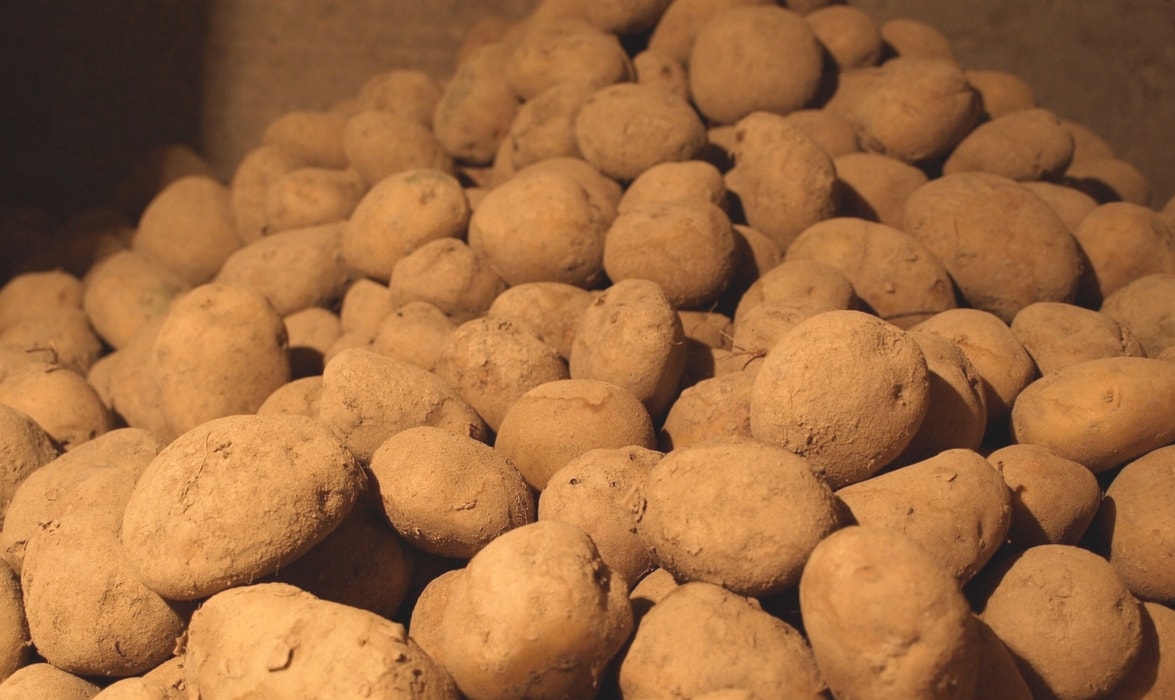
A cellar, provided it is healthy, has the advantage of preserving food from light, in a cool yet ventilated atmosphere. It is the ideal place to store root vegetables such as potatoes, carrots, celeriac.
A garage can serve as a substitute for the cellar if it is dark and remains frost-free.
In the freezer
This well-known method is quick and allows you to keep fruits and vegetables for several months. It is easy and convenient and generally only requires a brief blanching (initial short cooking) beforehand. However, freezing is sometimes criticised for altering the texture of certain vegetables, a drawback you can avoid by growing varieties known for their suitability for freezing.
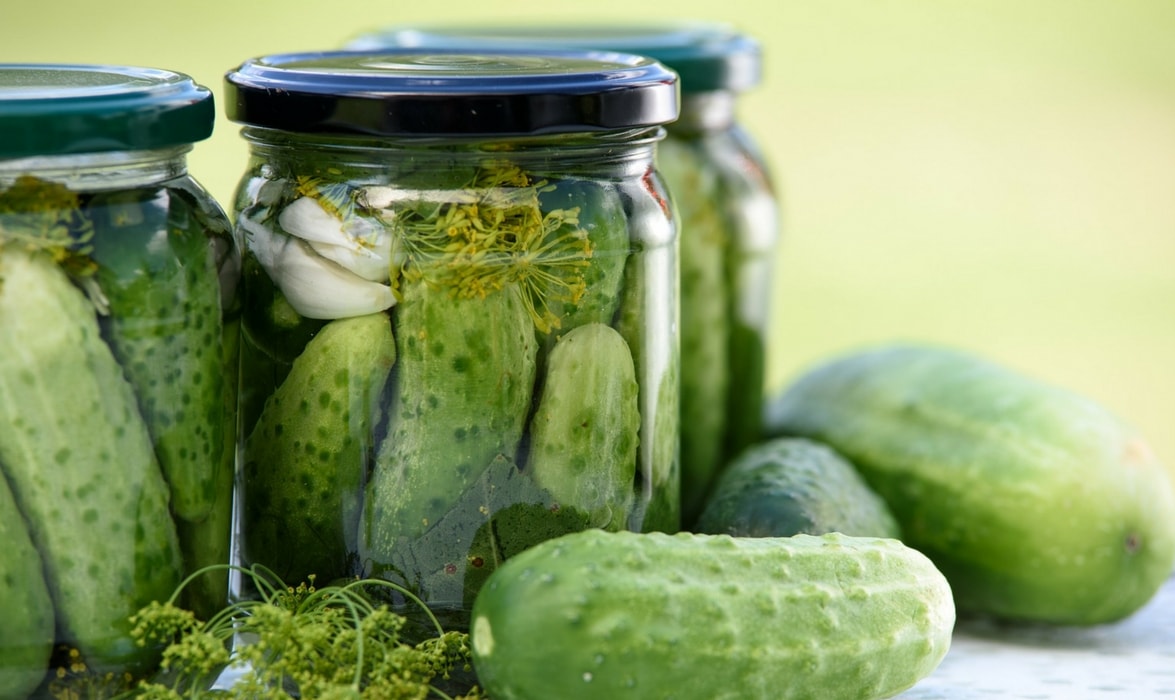
In jars
Making your own preserves is an excellent way to store your harvest. The range of possibilities is immense, as you can store raw or pre-cooked vegetables. Preservation can be done naturally, through lacto-fermentation, in oil, vinegar, alcohol, and sugar (jams), and almost all vegetables are suitable for this.
Once made, jars should ideally be stored in a dry, cool place away from direct light.
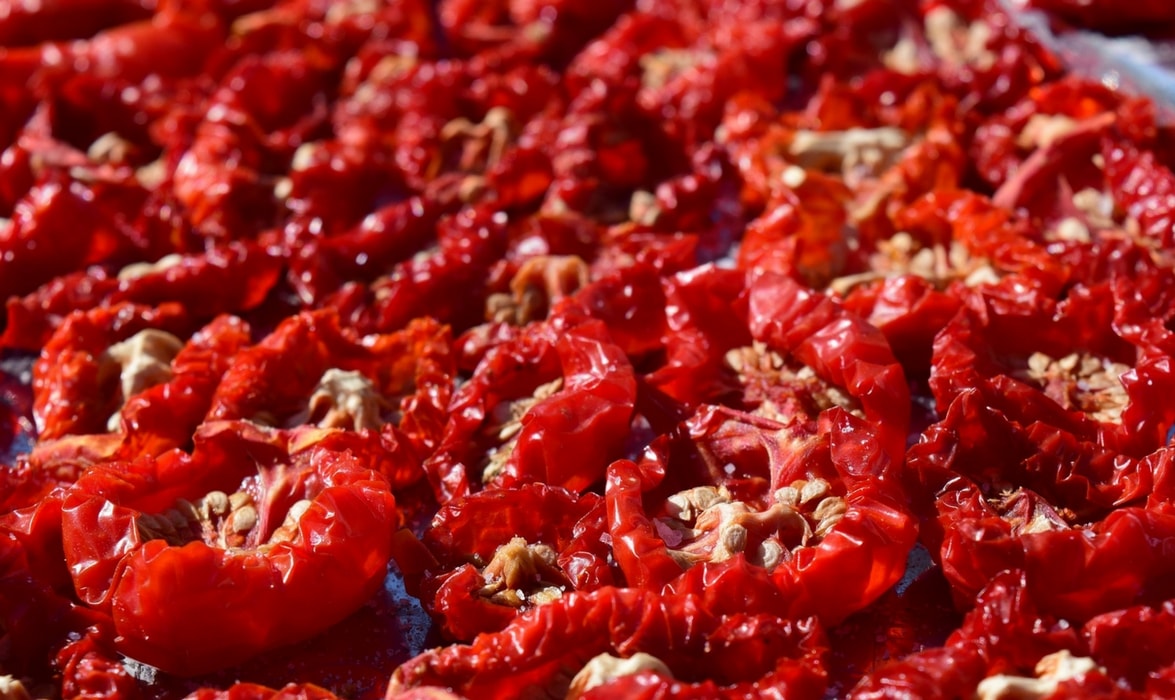
In boxes or packets, after dehydration or air drying.
Air drying is commonly used to preserve aromatic plants (thyme, rosemary, mint, lemon balm…), but dehydration, which allows for drying sliced or chopped vegetables, is less well known. For this, gentle heat from an oven equipped with a “fan-assisted” option or a food dehydrator is used. Many vegetables lend themselves to dehydration, with tomatoes and peppers being the most common.
Discover our tips for making dried or confit tomatoes.
- Subscribe!
- Contents













































Comments