
How to create a vegetable garden in acidic soil?
Tips and suitable vegetable plants
Contents
If you wish to start growing a vegetable garden in your garden, it is first important to know the acidity of your soil. Indeed, not all vegetable plants have the same needs, and they do not all grow in the same way depending on environmental conditions. Growth, development and productivity are thus directly impacted by the acidity of the vegetable garden. Acidic soils are known to have some fertility drawbacks. However, they also have advantages, and many plants thrive in them without any issues. If necessary, certain methods can help rebalance the soil pH.
Here you will find all our tips for creating a vegetable garden in acidic soil.
How to tell if the soil in your vegetable garden is acidic?
Chemically speaking, soil is defined by its alkalinity and acidity, which are measured using pH. This unit of measurement ranges from 1 to 14. The nature of your soil’s pH directly depends on the type of rock found in the subsoil, as well as its composition (clay, silt, etc.), its limestone content, and your own contributions of fertiliser.
P.S. Acidic as red to yellow, neutral as yellow to green, and alcaline on the right, mainly in blue shades
What is an acid soil?
A soil with a pH between 6.9 < pH < 7.2 offers fertile ground, with rich microbial life, allowing for optimal nutrient assimilation by the plants growing in it. In contrast, when the soil pH is below 7 (3.5 < pH < 6.8), it indicates that the soil is acid. A soil with a pH above 7 (7.3 < pH < 9.0) is referred to as basic or alkaline.
Let’s focus here on acid soils. Note that these can be as varied as they are numerous, since the soil can be only slightly acid (5 < pH < 6), which is the most common situation, and thus without real consequences for your vegetable plants. However, the soil can also exhibit critical acidity, or even be downright peaty (5 < pH < 3.5), a much rarer situation.
How to recognise an acid soil?
Carefully observe the vegetation that grows spontaneously at the location of your future vegetable garden. Some plants particularly thrive in acid environments, including:
- heathers;
- bracken ferns;
- creeping buttercups;
- chestnuts;
- foxgloves;
- broom;
- blueberries;
- nettles;
- and meadow sorrel.
These acidophilous plants are good indicators of soil acidity. Other signs include that acid soils generally have a darker colour. Heather soil and sandy soils are also predominantly acid.
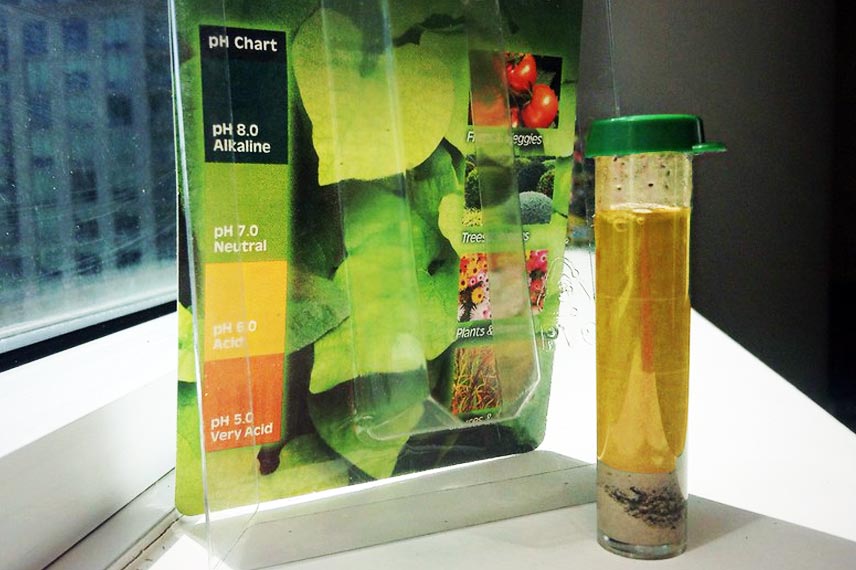

While these indicators can be good clues, only the analysis of a soil sample from your vegetable garden can accurately determine the pH level of your soil. There are analysis kits available that can be easily found in garden centres, which allow for precise measurement of a soil’s pH.
To learn more, check out our article: Acid soil, neutral soil or calcareous soil: how to tell?
What are the disadvantages of acidic soil in the vegetable garden?
It is first very interesting to highlight that the soils richest in humus are often acidic. These soils, perfect for a vegetable garden, have a pH ranging between 5.6 and 6.6. No correction is necessary if the soil in your vegetable garden has this level of acidity. Indeed, the biological activity of such soil, as well as its nutrients, is quite normal.
On the other hand, growing a vegetable garden in very acidic soil (pH below 5.6) has many disadvantages. To begin with, this type of soil has lower biological activity. As a result, microorganisms such as bacterium, yeasts, and fungi operate at a slower pace. The soil is then low in humus and organic matter decomposes very slowly. Similarly, there are far fewer earthworms, beetles, myriapods, etc. Furthermore, the nutrients (nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus, and trace elements) do not reach the plants. These are essential elements for the growth of your vegetables and fruits, which then suffer from deficiencies and are more susceptible to diseases. Finally, very acidic soil increases the rate of absorption of metallic ions by plants (aluminium, copper, lead, cadmium, mercury…). Metals that can be harmful to health, and which we would prefer to avoid in our vegetables!
Discover other Vegetable gardens
View all →Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Which vegetables can be planted in acidic soil?
A moderately acid soil is not a real problem in the vegetable garden, as long as you choose vegetable plants that appreciate its characteristics.
Vegetables to favour in slightly acid soil
If your soil has a pH between 6 and 7, it means it is perfectly balanced and provides good mineral nutrition for the plants growing in it. In this case, you are practically unrestricted in your planting choices, as most plants thrive very well.

- On the fruit and vegetable side, do not hesitate to grow all varieties of cabbages, as well as asparagus, Swiss chard, celery, radishes, tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, beans, lettuces, and strawberries.
- In terms of aromatic herbs, plant garlic, basil, chives, or thyme.
- Enhance the edges of your vegetable garden with flowers to attract pollinators, such as scented peas, asters, chrysanthemums, dahlias, gladioli, hyacinths, or roses.
Vegetables to favour in acid soil
The range of options in more acid soils, with a pH between 5 and 6, is somewhat more limited. Therefore, focus on acidophilous vegetables that have high iron requirements.
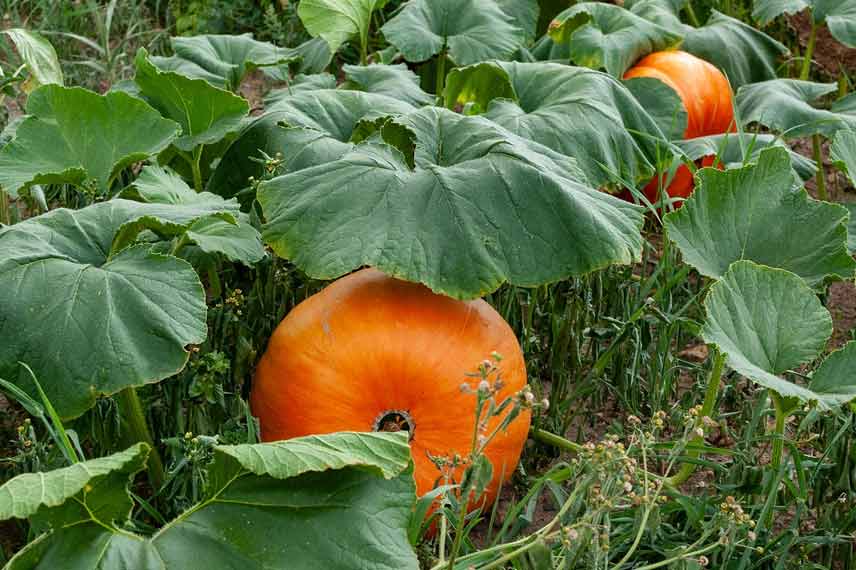

- On the fruit and vegetable side, grow potatoes and squashes (which particularly appreciate acid mediums), carrots, parsnips, artichokes, spinach, chillies, and shallots, as well as rhubarb, and raspberries, blackberries, blueberries, and cranberries.
- In terms of aromatic herbs, plant fennel, parsley, sorrel, and chives.
- For flowers, install coreopsis, cosmos, and irises around the vegetable garden.
However, absolutely avoid growing cabbages, thyme, poppies, geraniums, lavenders, mustard, centauries, primroses, and hellebores there.
And in very acid soils?
If the pH of your soil is below 5, unfortunately, you will not be able to sow anything in its current state. Therefore, refer to our advice on how to rectify the pH of overly acid soil.
How to rebalance the acidic soil of a vegetable garden?
To achieve a good yield in the vegetable garden, it is sometimes necessary to get as close as possible to a neutral pH. A thorough analysis of your soil is therefore absolutely essential to ensure its exact characteristics.
To rebalance the overly acidic soil in your vegetable garden, various solutions are available to you.
Amend the soil
You can add a basic amendment to the soil, but do so sparingly to avoid causing an opposite imbalance. Here, opt for an amendment rich in limestone, as the basic soil is precisely lacking in this. This will lighten the soil while raising the pH. Dolomite, wood ash, agricultural lime, marl, crushed limestone, or even lithothamnium… are all products to consider here. Carry out the amendment in autumn, or at the very beginning of winter, by incorporating it into the soil through light raking. Then water the vegetable garden area regularly to ensure the amendment is active. If the soil is very acidic, be aware that rebalancing will require patience, as the operation will likely need to be repeated over several years. Another option is to incorporate well-decomposed compost into the soil of the vegetable garden, again through light raking. Mature compost indeed has the ability to neutralise the soil.
Plant a cover crop
Another solution is that you can sow a cover crop in the location of your future vegetable garden. This will help to correct the acidity as well as the structure of your soil. Compose your cover crop by combining various plantings of lupin, melilot, millet, or even buckwheat.
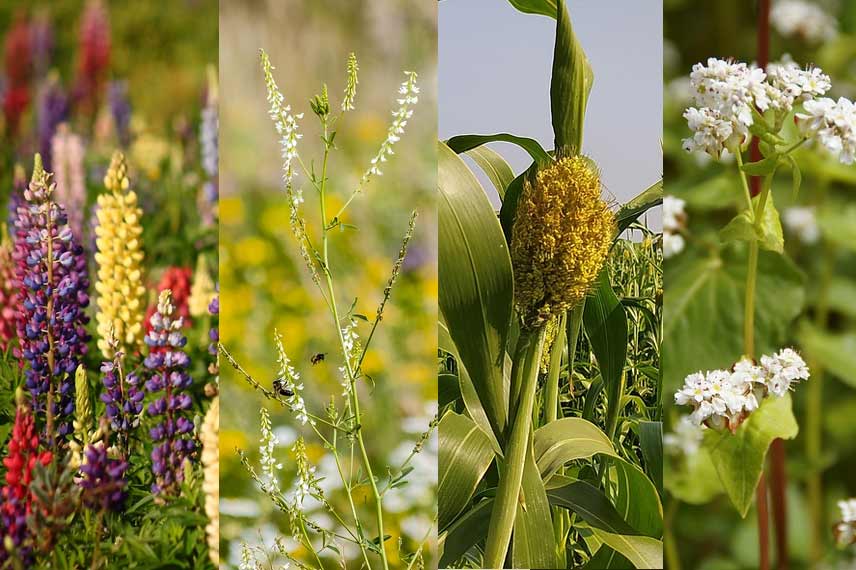

Rely on the effect of time and nature
Lastly, you can simply let nature take its course. Of course, this option is particularly restful for the gardener, but it is also the longest. Do not intervene and allow the existing vegetation to naturally rebalance the soil’s pH. The duration of the “treatment” can vary greatly, from one year to several years depending on the case. However, it will be easy to observe the effects, as acidophilous plants will eventually disappear in favour of neutrophilous plants.
- Subscribe!
- Contents










































Comments