
Diseases and Pests of the Almond Tree
Detecting and treating them naturally
Contents
Appreciated for its wonderful spring flowering and especially for its tasty fruits, the almond tree is a proud representative of Mediterranean flora. Particularly resilient and undemanding, it is suited to even the most challenging growing conditions; however, it can still be subject to attacks from diseases or pests.
Is your almond tree showing signs of weakness, and do you suspect that little critters or diseases are to blame? Want to know how to recognise a sick almond tree? Don’t panic: we list here the main sources of attacks on almond trees and how to remedy them.

Almond tree, Prunus dulcis
→ To become an expert in almond tree cultivation, feel free to consult our complete guide: THE ALMOND TREE: PLANTING, PRUNING, HARVESTING
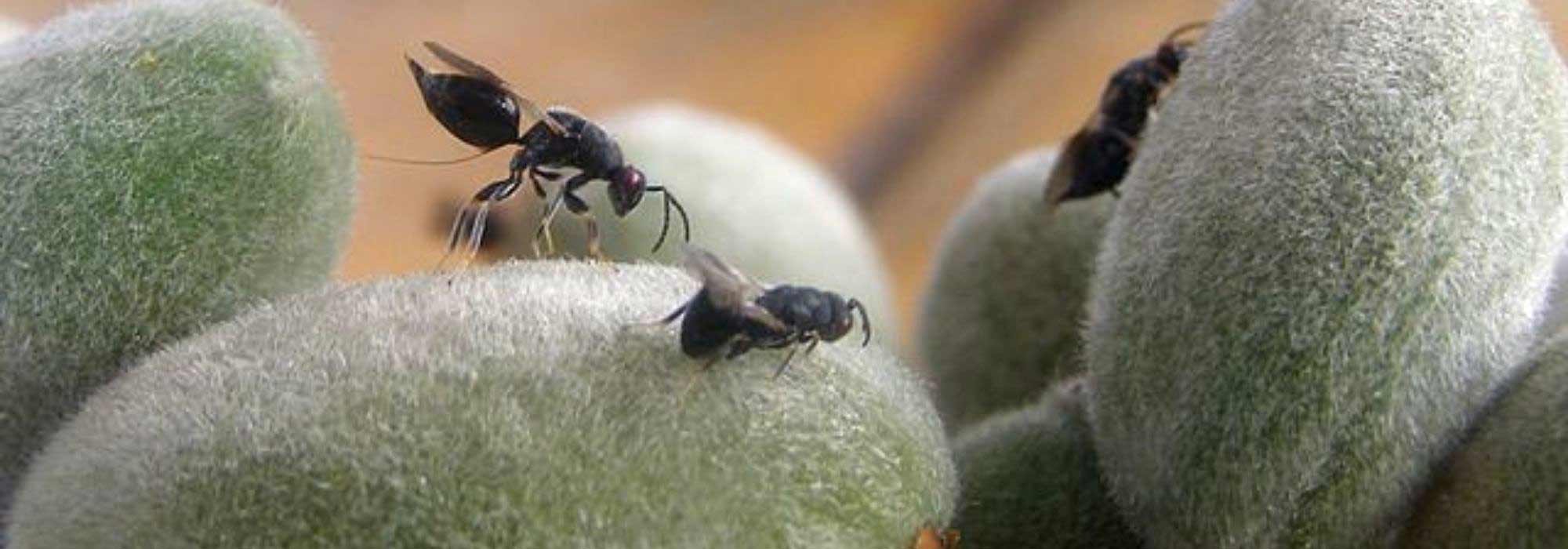
The almond wasp
“`html
Symptoms and Cause
Observed in France since the early 1980s, this hymenopteran from the Near East causes significant damage to almond production in France, potentially reaching up to 80% of the harvests. Eurytoma amygdali, is a black wasp where adult females measure 7 to 8 mm while males range from 4 to 6 mm.
This pest overwinters as a larva in the fruits left on the trees. Adults emerge by boring a small hole in the shell from early April to late May, depending on the region. After mating, females lay eggs inside the still tender almonds by piercing them, and a translucent gum exudation appears at the site of the injury. One or more larvae develop within the fruit.
Damage is visible from early June with the appearance of gum on the surface of the fruit. The contaminated fruits then remain attached to the tree and blacken during winter.
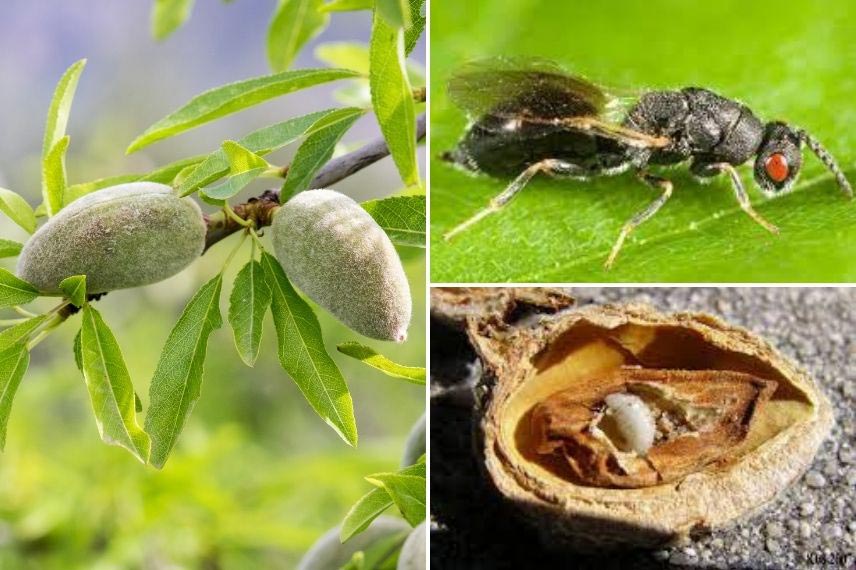

Almond tree, Prunus dulcis, wasp and larva of Eurytoma amygdali in an almond in August (Commons Wikimedia)
Preventive Measures and Treatment
- Remove almonds that show signs of attack (they appear dehydrated and have a brownish colour)
- In winter, destroy contaminated almonds left on the tree
- Installing insect nets for orchards creates a physical barrier between the trees and the wasps, preventing them from laying eggs in the fruits
- Clay sprays, in the form of calcined kaolinite, can have a preventive role and act mechanically as a mineral barrier disrupting the pest’s behaviour. This method is particularly used against cherry and olive flies
- Some organic fruit growers use sprays of essential oil solutions from clove, geranium, and juniper with black soap (2 L/ha) diluted in water (480 L/ha). As soon as the wasps start to emerge, the almond trees are treated once a week for 5 weeks.
“`
Fusicoccum canker
Symptoms and Cause
This canker is a disease caused by the fungus Fusicoccum amygdali. Affecting peach trees, it can also impact almond trees and cause significant damage, as the disease is difficult to eradicate. The canker fungus penetrates trees through buds, flower petals, young fruits, and leaves. It then emits a toxin that causes wilting of the affected organs. Wilting of young shoots is observed, and from the bud burst period: young leaves, flowers, and young almonds wilt and dry out. Growth and dispersion of spores are favoured by warm, humid weather.
Preventive Measures and Treatment
- Prune and destroy the shoots and leaves affected by the fungus
- Avoid any nutritional imbalance in the tree, particularly by avoiding excess nitrogen
- Avoid watering directly on the almond tree
- Be vigilant during pruning, as the fungus primarily enters through wounds. Use well-sharpened and disinfected tools
- Spray your almond tree with Bordeaux mixture, which has fungicidal action.
→ Find our article on canker of trees and fruit trees: treatments and control
Discover other Almond trees
View all →Available in 2 sizes

Available in 2 sizes
Available in 3 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 2 sizes
Available in 1 sizes

Available in 2 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Moniliosis
Symptoms and Cause
Brown rot is the generic name for various fungal diseases of fruit trees caused by different species of fungi. The almond tree is affected by Monilinia laxa, which primarily targets stone fruits. Brown rot mainly affects damaged fruits, and a humid climate during flowering promotes its occurrence. Fruits rot on the tree and often remain mummified without falling.
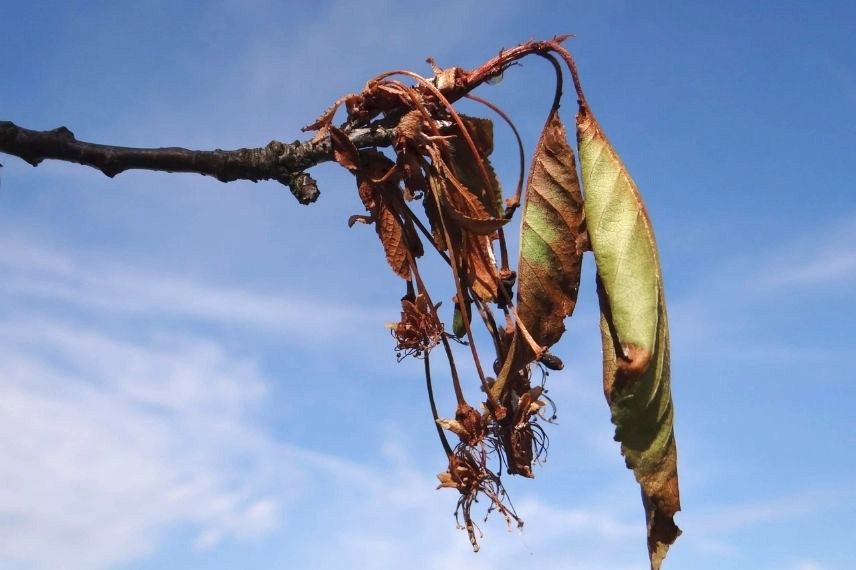

Branch affected by brown rot
Preventive Measures and Treatment
- To prevent the spread of Monilinia, dispose of infected fruits and branches at a waste disposal site
- Wash your hands thoroughly after handling infected parts and disinfect tools that have come into contact
- As the fungus overwinters in the crevices or wounds of trees, a treatment with lime water or Bordeaux mixture can be beneficial.
→ Brown rot of fruit trees – PREVENTING AND TREATING THIS DISEASE
Read also
How to harvest and store almonds?Coryneum leaf spot
Symptoms and Cause
Another disease caused by a fungus: Coryneum beijerinckii. The common name for this infection is “Coryneum Shot Hole” or “Shot Hole Disease“. It affects almond trees, as well as Plums, Cherries, and Peaches. The disease attacks both the leaves, the shoots, and the stones. Circular spots about 3 mm in diameter with a grey necrotic centre and a purple border appear on the leaves of almond trees, then transform into perforations, hence the name shot hole. On the shoots, the spots also surround a necrotic centre that will persist and lead to a canker. The stones also exhibit numerous spots.
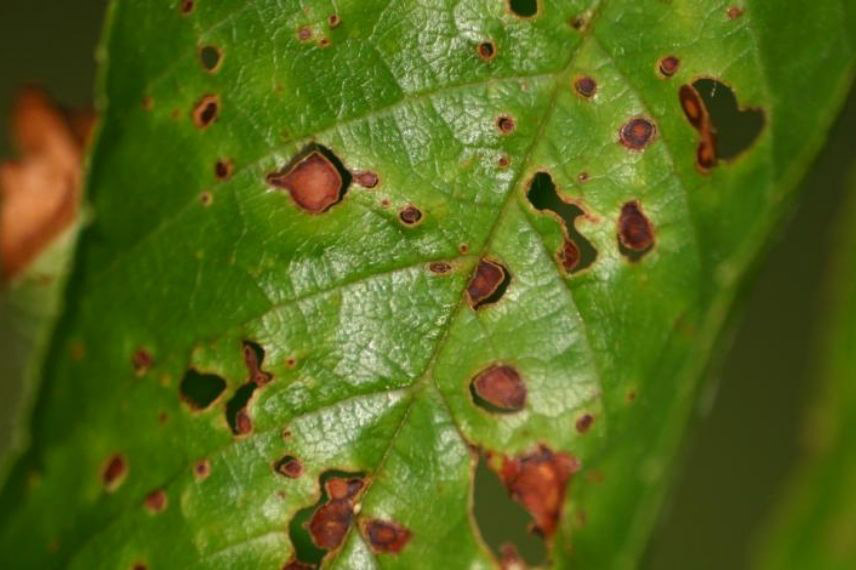

Leaf affected by Coryneum Shot Hole
Preventive Measures and Treatment
- Remove canker-infected shoots before and after winter
- Avoid overhead watering
- As the fungus overwinters in the cankers and buds of the affected shoots, where it survives from year to year, a treatment with lime water or Bordeaux mixture may be beneficial.
→ Find our article on Coryneum or Shot Hole of Stone Fruit Trees
The Red Mite of the Almond Tree
Symptoms and Cause
Phyllocoptes graniti, also known as the almond phytopt, is a red mite specific to this tree. Measuring 3 to 5 mm, it is barely visible to the naked eye and can cause significant damage when the weather is dry and hot. Females are dark red, while males are lighter, more orange in colour. The eggs are also red, and up to ten generations can succeed one another in a single season.
In April and May, the eggs that have wintered on the wood hatch, and the larvae develop on the leaves until they become adults by mid-May. The affected leaves turn brown and then take on a characteristic greyish hue. Photosynthesis can no longer occur. During severe infestations, leaf drop in almond trees is observed, along with a reduction in almond size.
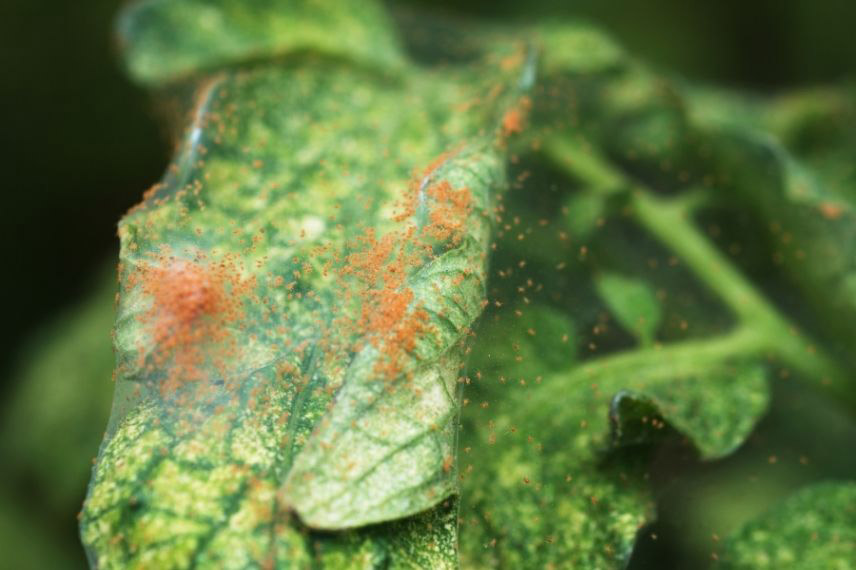
Infested leaf with red mites
Preventive Measures and Treatment
- Spray the foliage with water during hot and dry weather
- Encouraging biodiversity in the garden helps to prevent the appearance of mites. Natural enemies of these pests, such as ladybirds and the mite Phytoseiulus, will help regulate them. They can also be found in biological control.
→ Find our article on Red Spider Mite: Identification and Treatment
- Subscribe!
- Contents








































Comments