
Climate zones and USDA zones in France
how to navigate effectively to choose the right plants
Contents
France is well known for the extraordinary diversity of its landscapes as well as its climates. Indeed, although enjoying a generally temperate climate, our country displays significant differences in temperatures and rainfall depending on the regions… In nature, this translates into quite specific floras and, in gardens, into the necessity of choosing suitable vegetation: particularly hardy plants, resistant to cold or those that thrive better in a mild and humid climate…
This information is present in all our plant profiles, but understanding it is not always easy as we refer to USDA zones.
I therefore propose to clarify the climatic zones in France as well as their translation into USDA zones to help you choose the plants suited to your garden’s climate!
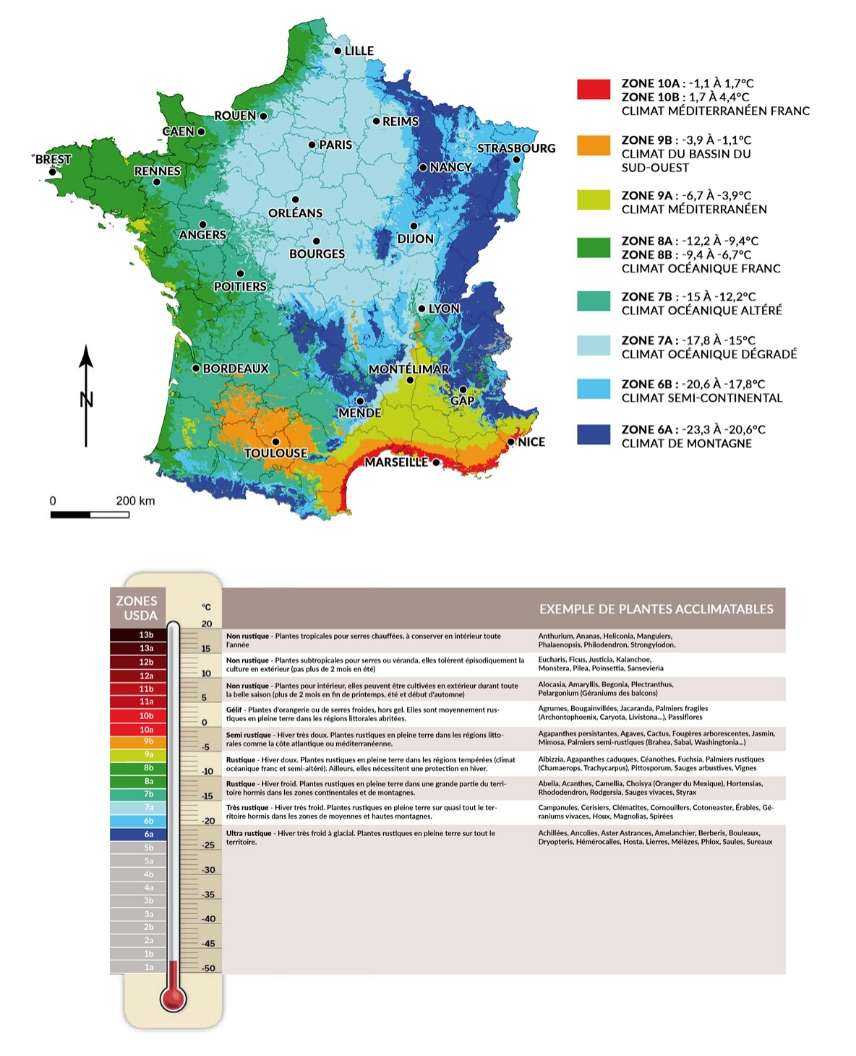
Climate map of France + USDA Zones
Read also
Hardy plants and hardinessUSDA Zones
The USDA zones concept is American, created by the United States Department of Agriculture (hence the name USDA). It is a geographical division into 26 hardiness zones based on the average minimum temperatures over the last 20 years. Essentially, these indicators reflect the “probable minimum temperature” that your region will experience in winter, which is crucial when discussing hardiness!
This approach to understanding hardiness zones is used in many countries, including France. The USDA zones have the advantage of being quite precise and are widely used around the world. The scale includes 26 levels, but in France, only 10 are used, from zone 6a to zone 10b.
Summary table:
| Climate type | USDA Zone |
| Type 1 Montane climate | Zone 6a: -23.3 to -20.6°C |
| Type 2 Semi-continental climate and montane margin climate | Zone 6b: -20.6 to -17.8°C |
| Type 3 Degraded oceanic climate of the Central and Northern plains | Zone 7a: -17.8 to -15°C |
| Type 4 Altered oceanic climate | Zone 7b: -15 to -12.2°C |
| Type 5 True oceanic climate | Zone 8a: -12.2 to -9.4°C |
| Zone 8b: -9.4 to -6.7°C | |
| Type 6 Altered Mediterranean climate | Zone 9a: -6.7 to -3.9°C |
| Type 7 Climate of the Southwestern Basin | Zone 9b: -3.9 to -1.1°C |
| Type 8 True Mediterranean climate | Zone 10a: -1.1 to 1.7°C |
| Zone 10b: 1.7 to 4.4°C |
Discover other Climbers
View all →Available in 0 sizes
Available in 0 sizes
Available in 0 sizes
Available in 0 sizes
Available in 0 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Available in 0 sizes
Available in 2 sizes
Available in 1 sizes
Type 1: Mountain Climates - USDA Zone 6a
Mountain climates are quite diverse and found throughout almost all of France: Pyrenees, Central Massif, Alps, Jura, Morvan, Ardennes, but also, at lower altitudes, the plateaux to the east of Champagne and part of Lorraine and Franche-Comté…
In these geographical areas, one can observe:
- a high number of days and a significant total of precipitation (rain, snow…)
- an average temperature below 9.4°C with more than 25 days during which the minimum temperature was below -5°C and fewer than 4 days with a maximum above 30°C.
- The interannual variability of July precipitation and winter and summer temperatures is at its maximum.
→ This climate corresponds to USDA zone 6a (minimum temperatures recorded: -23.3 to -20.6°C)
Read also
10 very hardy, frost-resistant treesType 2: semi-continental climate and montane margin climate - USDA Zone 6b
The type 2 climate is an intermediate climate between montane climates and types 3, 4, and 8. The area affected by this climate includes the montane peripheries and extends over vast regions in Burgundy, Lorraine, and Alsace.
In these areas:
- temperatures are less cold than in the mountains (but, at the same altitude, colder than anywhere else),
- precipitation is slightly lower and less frequent,
- there is a low ratio between autumn and summer precipitation
→ This climate corresponds to USDA zone 6b (minimum recorded temperatures: -20.6 to -17.8°C)

Type 3: the degraded oceanic climate of the plains of the Centre and North - USDA Zone 7a
The climate type 3 concerns the entire Paris Basin with an extension to the south (middle Loire valley, northern Massif Central, and Saône valley).
The climate remains oceanic but with notable variations:
- temperatures are intermediate (around 11°C on average annually, between 8 and 14 days with a temperature below -5°C).
- precipitation is low (less than 700 mm of annual total), especially in summer, but rain falls on average for 12 days in January and 8 days in July, average values compared to the whole of France.
- the interannual variability of precipitation is minimal while that of temperatures is high.
→ This climate corresponds to USDA zone 7a(minimum recorded temperatures: -17.8 to -15°C)
Type 4: Altered Oceanic Climate - USDA Zone 7b
The climate type 4, altered oceanic climate, appears as a transition between the true oceanic (type 5) and degraded oceanic (type 3). Between Nord-Pas-de-Calais and Normandy, it forms a narrow band, while to the west, this transition widens to over 150 km. This climate also affects the south-west of the Massif Central, from Dordogne to Aveyron and the north of the Pyrenees.
The characteristics:
- The average annual temperature is quite high (12.5°C) with a low number of cold days (between 4 and 8 per year) and a sustained number of warm days (between 15 and 23 per year).
- The annual temperature range (July-January) is close to the minimum, and the average interannual variability.
- Precipitation, with an annual cumulative average (800-900 mm), mainly falls in winter, with summer being relatively dry.
→ This climate corresponds to USDA zone 7b (minimum recorded temperatures: -15 to -12.2°C)
Type 5: The oceanic climate - USDA Zones 8a and 8b
The oceanic climate occupies a narrow strip along the North Sea and encompasses all of Normandy, Brittany, Vendée, and Charentes. A small oceanic area covers the west of the heaths and Pyrénées-Atlantiques.
In these areas:
- temperatures are moderate and very homothermal: the annual range (less than 13°C difference between July and January), the number of cold days (fewer than 4) and hot days (fewer than 4), and interannual variability are minimal.
- Annual precipitation is abundant (just over 1000 mm) and frequent in winter (more than 13 days in January).
- Summer is also rainy (8-9 days in July) but the totals are low.
- The oceanic climate is also characterised by a high interannual variation in winter precipitation.
→ This climate corresponds to USDA zones 8a and 8b (minimum recorded temperatures: -12.2°C to -6.7°C)

Type 6: Altered Mediterranean Climate - USDA Zone 9a
The altered Mediterranean climate mainly extends over the southern Alps and Pre-Alps, encompassing most of the two departments of Alpes-de-Haute-Provence and Drôme. It is also distinguished by a few remnants on the left bank of the Rhône, near Ardèche and in the form of a narrow strip to the west, between the Eastern Pyrenees and Hérault.
The characteristics:
- an elevated average annual temperature, with a limited number of cold days and warm days ranging from 15 to 23 per year.
- minimal interannual variability of July temperatures: summers are consistently hot from year to year.
- a mean annual precipitation total (800-950 mm) but not distributed in a homogeneous manner.
- autumn and winter, humid and highly variable from year to year, contrast with summer, which is dry and stable based on the 1971-2000 average.
→ This climate corresponds to USDA zone 9a (minimum recorded temperatures: -6.7 to -3.9°C)
Type 7: The climate of the South-West Basin - USDA Zone 9b
This type of climate pertains to a geographically disparate area, straddling several regions (Aquitaine, Languedoc) and centred around the middle basin of the Garonne, conveniently referred to as the “South-West Basin.”
It is characterised by:
- a high annual average temperature (above 13°C) and a high number (> 23) of warm days, while days with a frost below -5°C are rare.
- a high annual temperature range (15 to 16°C) and low interannual variability of winter and summer temperatures.
- Precipitation, which is low in annual total (less than 800 mm) and in winter, is somewhat higher during summer. It is more frequent in winter (9-11 days) than in summer (fewer than 6 days). This distribution indicates that the intensity of precipitation is low in winter (oceanic precipitation) and higher in summer (thunderstorm disturbances coming from Spain or the Bay of Biscay). The interannual variability of precipitation is moderate.
→ This climate corresponds to USDA zone 9b (minimum recorded temperatures: -3.9 to -1.1°C)

Type 8: Mediterranean climate - USDA Zones 10a and 10b
This climate occupies a band of around a hundred kilometres around the Mediterranean Sea, from the Pyrenees to the Var. Beyond this, in the Maritime Alps, the Mediterranean climate narrows to the point where it only appears punctate within the alpine valleys.
The climatic characteristics are very pronounced, more so than in each of the previous seven climates.
- Annual temperatures are high, cold days are extremely rare, and warm days are frequent.
- The interannual amplitude is significant (over 17°C between July and January), while these characteristics are very stable from year to year.
- The very high ratio of autumn to summer precipitation (> 6) is the main characteristic of this climate. The annual total of precipitation is low, with an arid summer but a rather well-watered winter despite a low number of rainy days. These characteristics are also stable from year to year.
→ This climate corresponds to USDA zones 10a and 10b (minimum recorded temperatures: -1°C to +4.4°C)
To find out more
Discover our advice sheet: Hardy plants and hardiness.
- Subscribe!
- Contents










































Comments